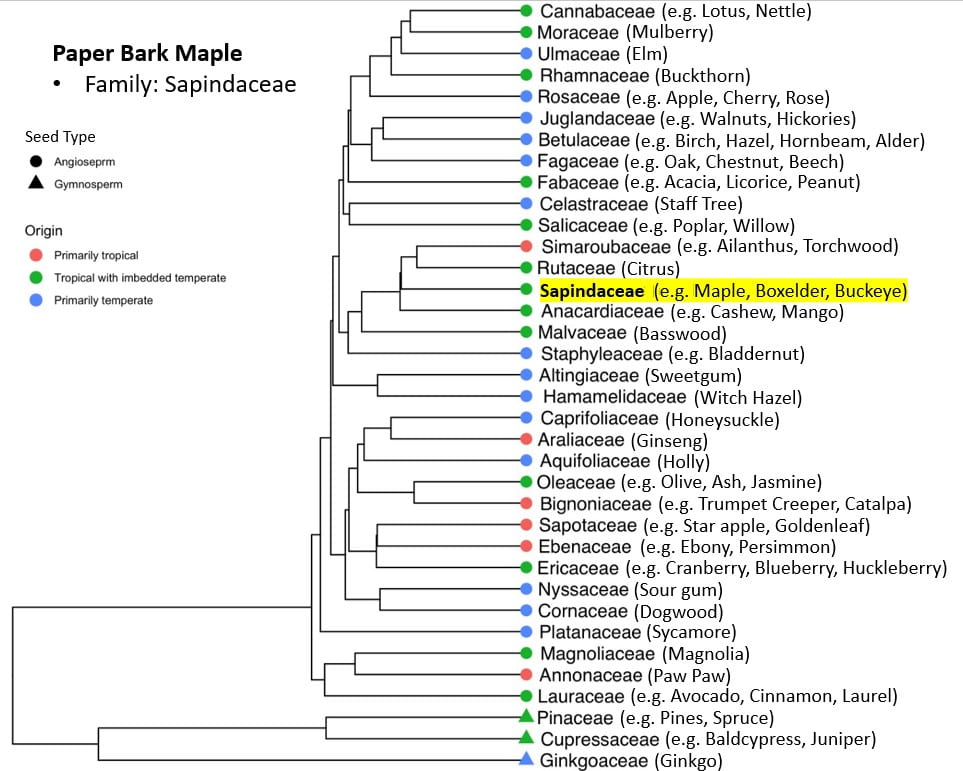
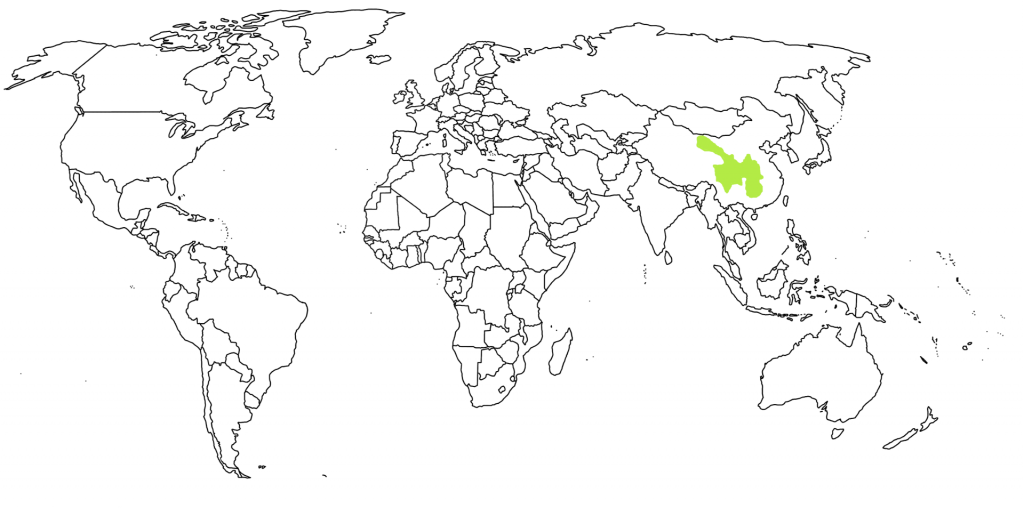
Paper Bark Maple
Arbor walk #36, TreeKeeper ID #3160

A type of maple originally native to the mixed forests of Central China, this species was introduced to the west through England in 1899 and transplanted to America soon after. It has since become endangered in its native range. Its most notable characteristic is its copper colored exfoliating bark, which peels off in attractive curls and often remains on the tree instead of falling to the ground.

GPS Coordinates
N/A
Percent Concrete
N/A
Distance to Buildings
| Year | Close Building #1 | Close Building #2 | Close Building #3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | DUC, 2.86 | Mallinkrodt, 33.78 | Simon Hall, 79.37 |
Distance to Other Species
| Year | Close Species #1 | Close Species # 2 | Close Species # 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Paper Bark Maple, 6.18 | Red Maple, 7.43 | Red Maple, 13.17 |
Standard Measurements
| Year | Height (m) | DBH (cm) | Caliper (m) | Crown Diameter N-S (m) | Crown Diameter E-W (m) | Average Crown Diameter (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 4.9886 | 6.4 | N/A | 3.64 | 3.51 | 3.575 |
| 2023 | 6.1 | 7.2/4.7 | N/A | 4.2 | 4.43 | 4.315 |
Nests and Pests
| Year | Description |
|---|---|
| 2020 | Lichen only present on one cut branch stump |
Leaf Identification
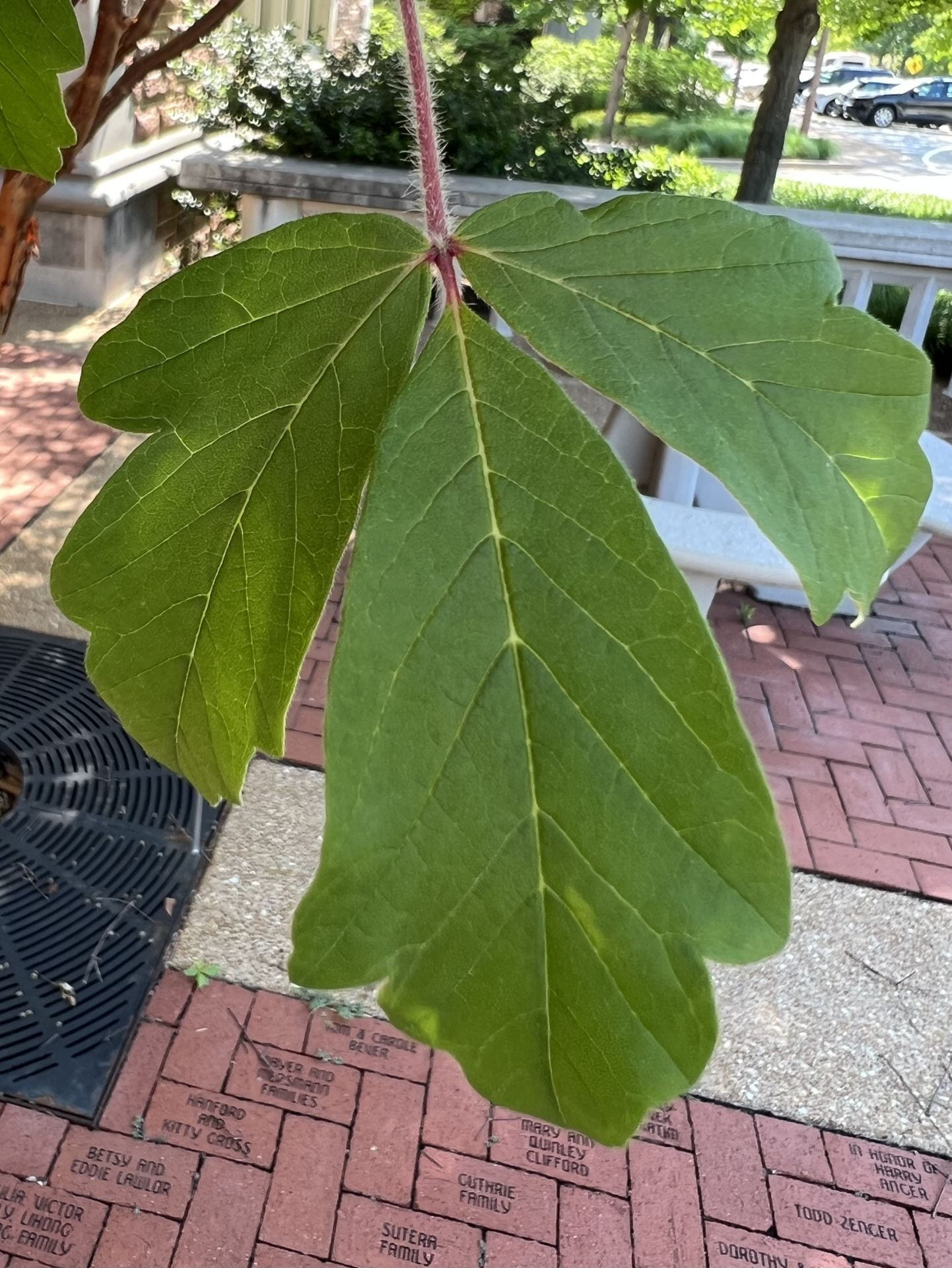
Unlike many maples, the Paper Bark Maple has compound leaves, set with two lateral leaflets at about 45 degrees each from the terminal leaflet. The leaflets are bright green, with 5-7 lobes that grow less distinct towards the tip. The underside of the leaf is pale green-white. The leaves are arranged opposite (paired at the stem).
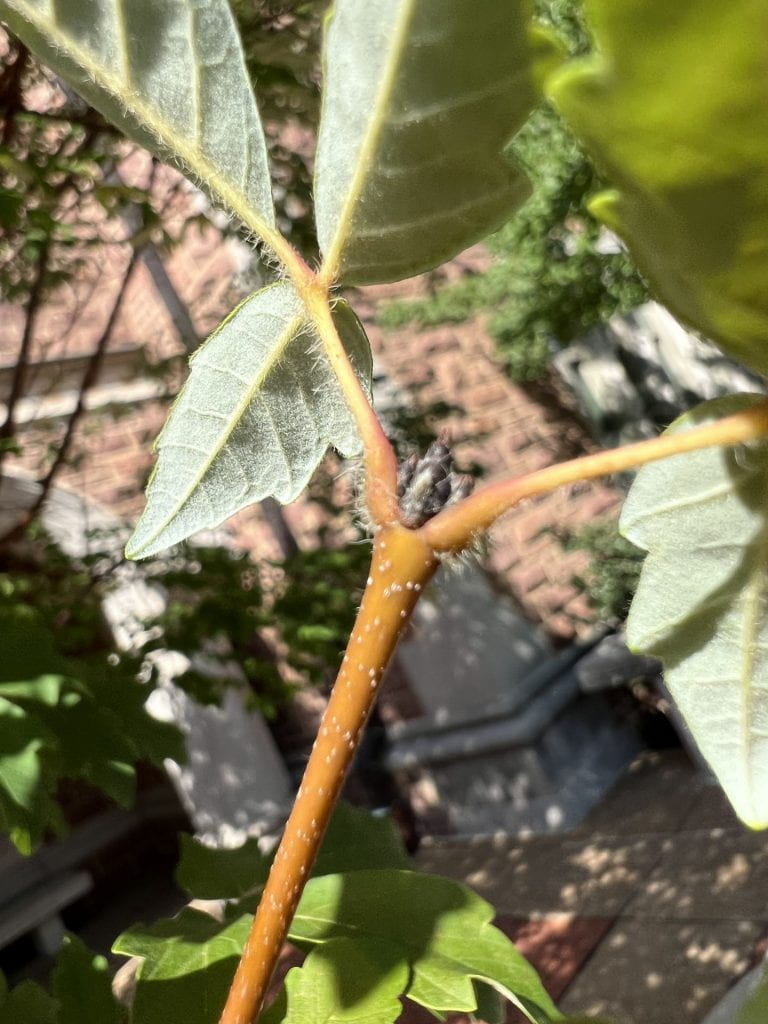
Twig and Bud Identification
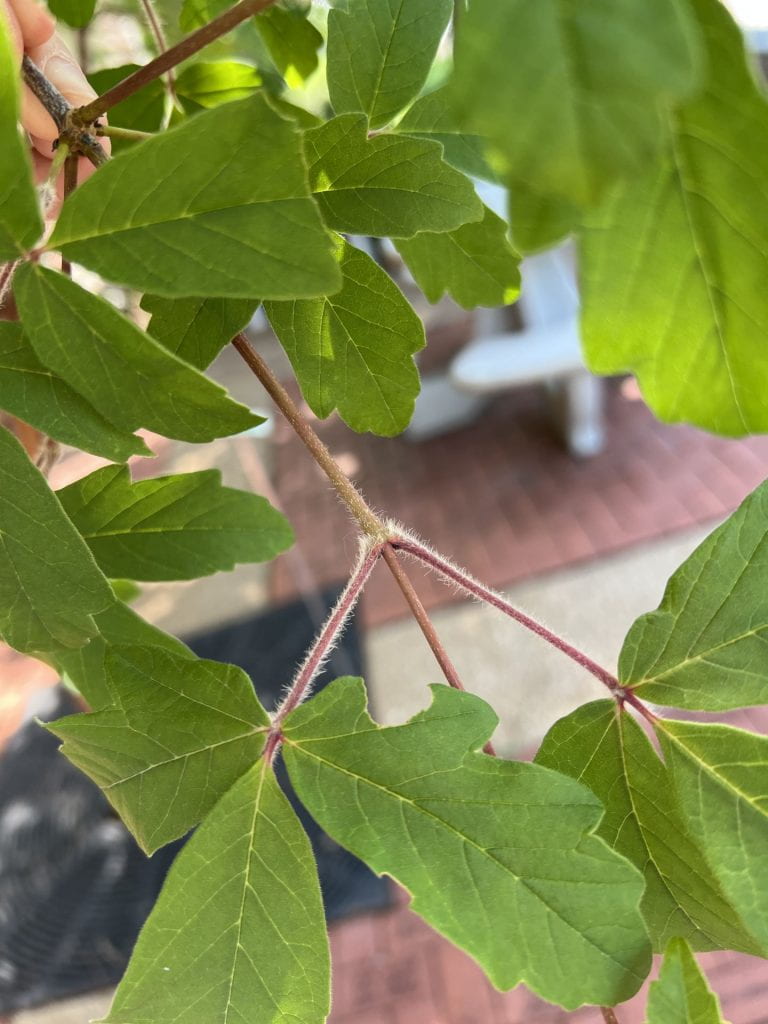
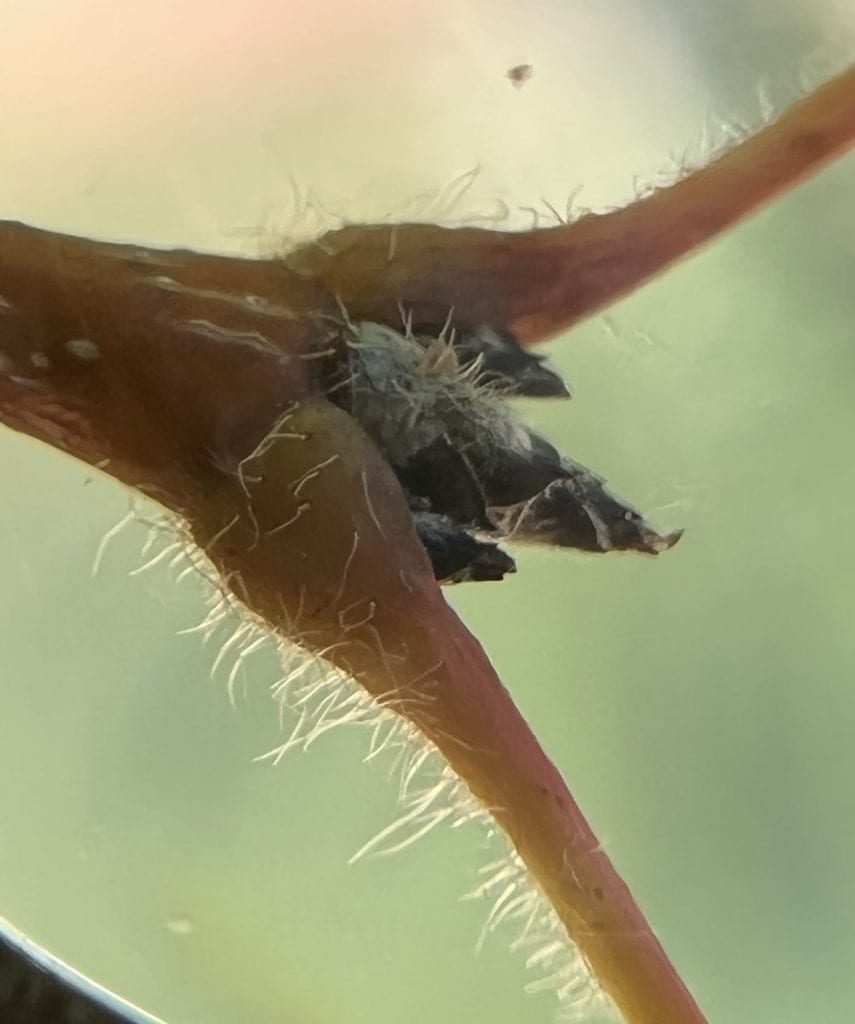
The twigs are orange-yellow with pale lenticels (pores), becoming red-tinged and hairy through the petioles of new leaves. The buds are dark brown, many-scaled, and pubescent (hairy) as well. The terminal buds are arranged in a cluster of three, with the middle bud being the longest.
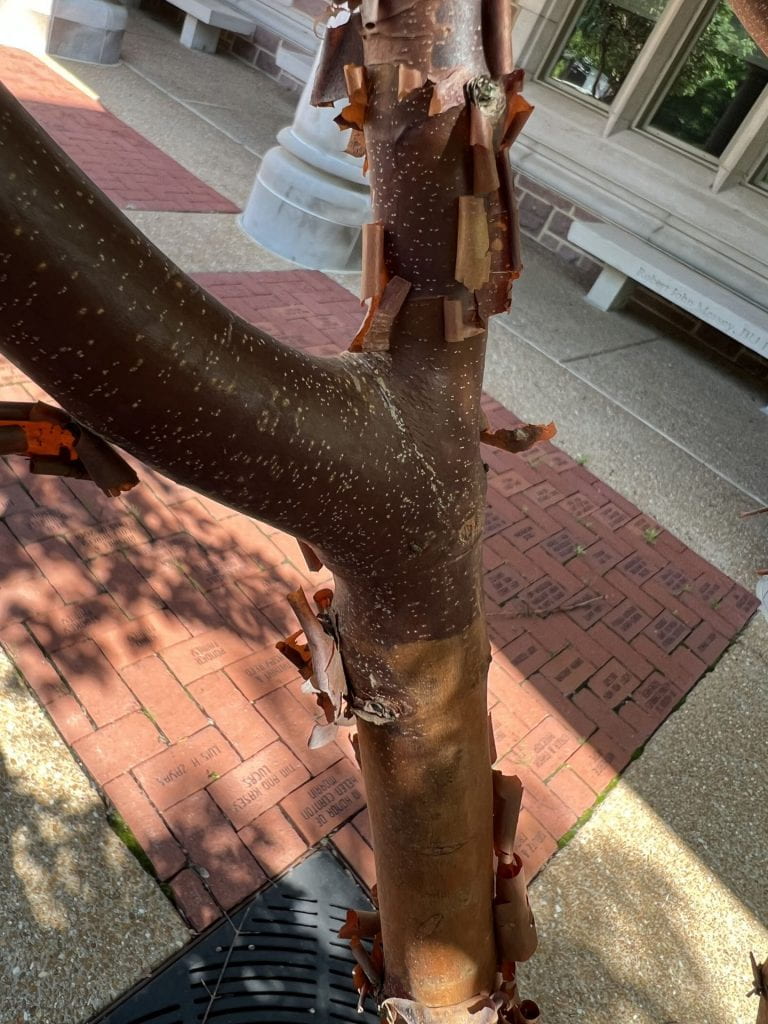
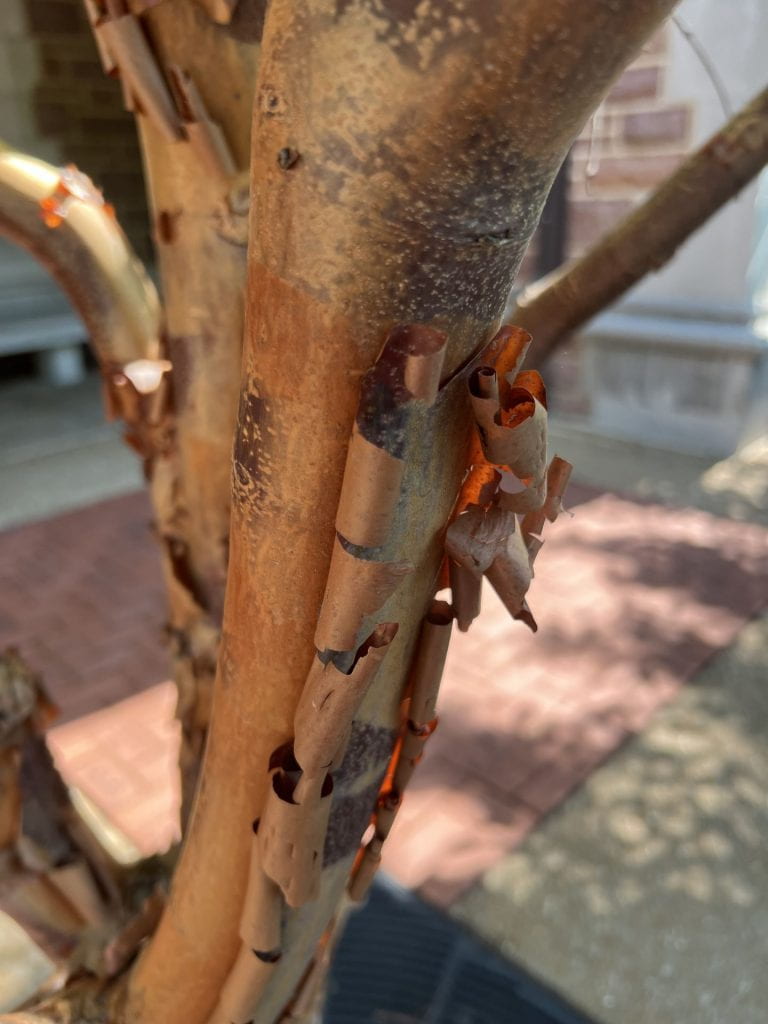
Bark Identification
The bark of the Paper Bark Maple is dark brown with white lenticels. The bark peels horizontally, leaving strips of papery bark curled up on the tree, and a orange-tan interior bark layer.
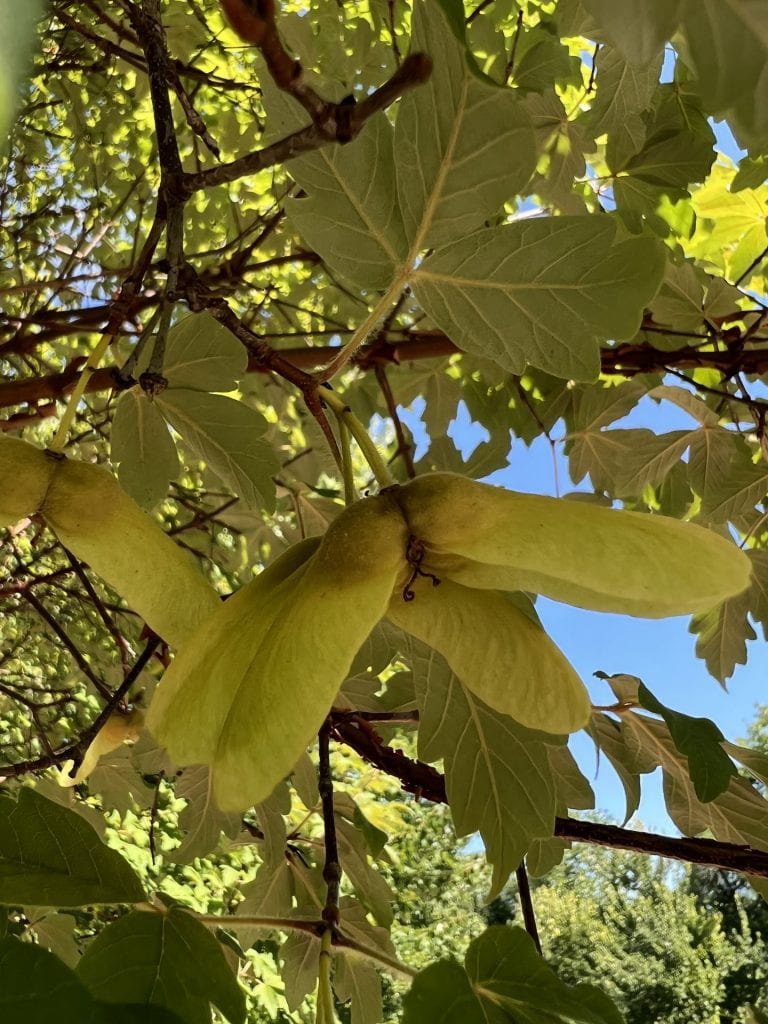
Fruit Identification
The fruit of the Paper Bark Maple is a double samara (papery winged seed coat). The samara matures from light green to brown, and is longer than most maples.
Flower Identification
The flowers of the Paper Bark Maple are inconspicuous and yellow, blooming in mid-spring. The flowers hang down from pubescent peduncles (flowering stems).