Persimmon
Arbor walk #70, TreeKeeper ID #3345

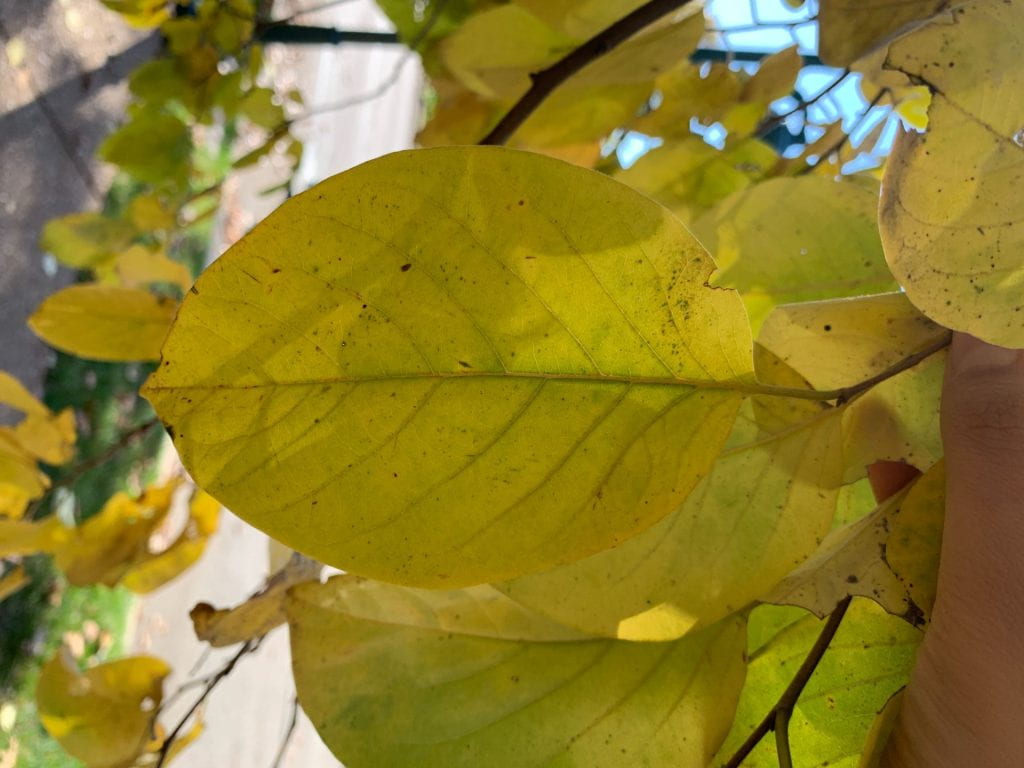
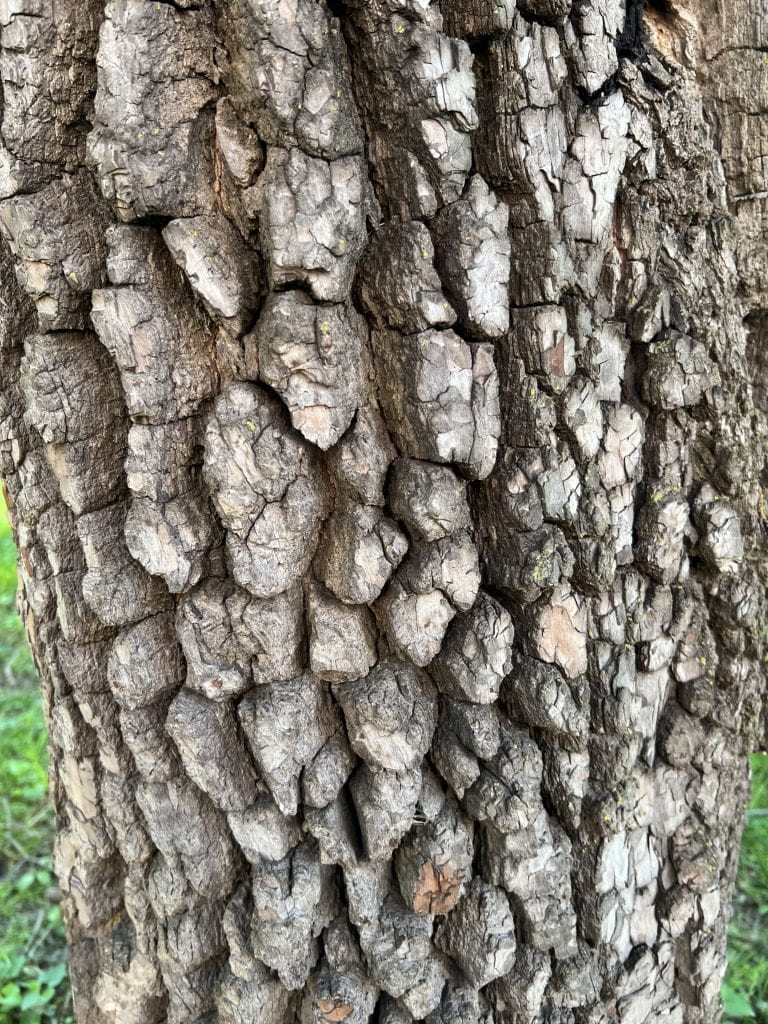
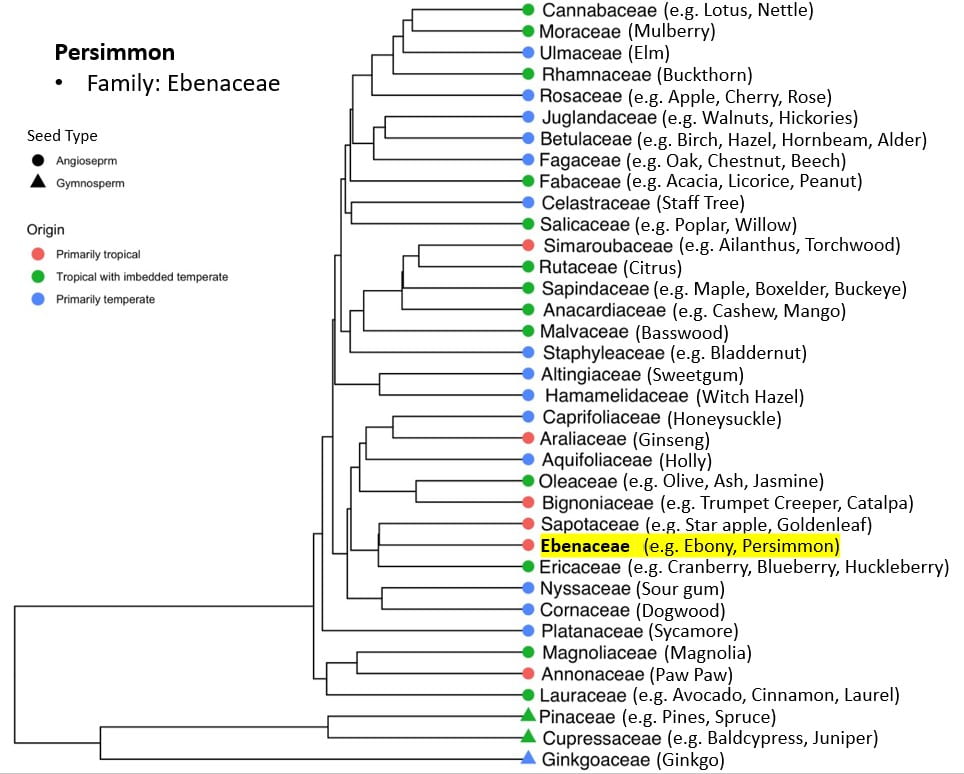
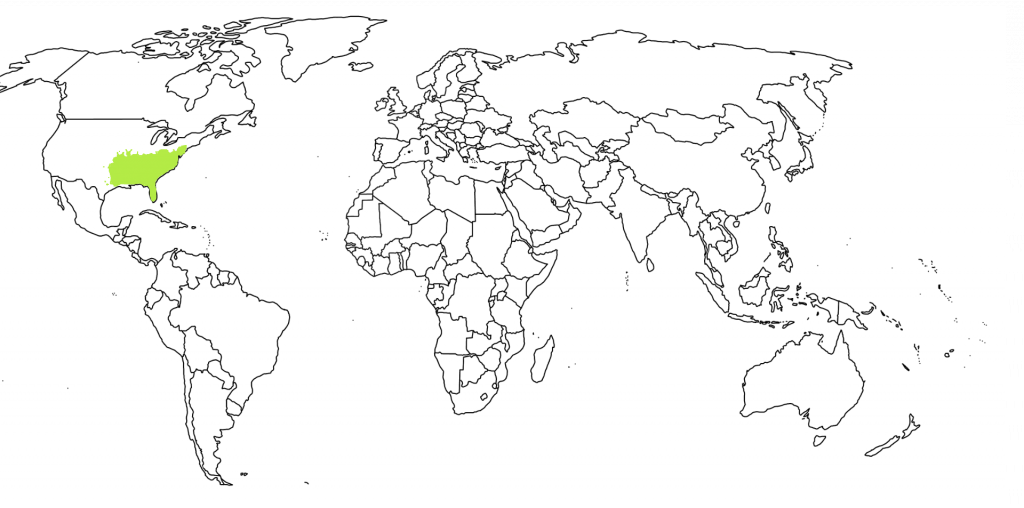
The Persimmon tree is native to the Southeastern U.S. and is easily recognized in winter by its unusual rugged, blocky bark. The tree’s thick, dark green leaves turn yellow in the Fall. Female trees produce large, orange-brown fleshy fruit that are edible after the first frost. It is important to resist the temptation to bite into the fruit before it falls to the group, as it probably is not ripe yet. Although commonly known for its fruit, the wood of the Persimmon is incredibly strong. It is commonly used to make golf clubs and billiard cues.

GPS Coordinates
N/A
Percent Concrete
N/A
Distance to Buildings
| Year | Close Building #1 | Close Building #2 | Close Building #3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Koenig House, 17.13 m | 3 University Ln, 23.26 m | Liggett House, 35.44 m |
Distance to Other Species
| Year | Close Species #1 | Close Species # 2 | Close Species # 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Sugar Maple, 5.65 m | American Holly, 5.96 m | Sugar Maple, 6.07 m |
Standard Measurements
| Year | Height (m) | DBH (cm) | Caliper (m) | Crown Diameter N-S (m) | Crown Diameter E-W (m) | Average Crown Diameter (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 16.9786 | 40.1 | N/A | 13.2 | 8.07 | 10.635 |
| 2023 | 16.69 | 42.7 | N/A | 14.2 | 10.6 | 12.4 |
Nests and Pests
| Year | Description |
|---|---|
| 2020 | Small, round borehole in an old cut plus many in the trunk A large gnarled, rotten indentation in the trunk bark Lots of green lichen on bark Some old ivy growing up the trunk |
| 2023 | Bagworms present |
Leaf Identification
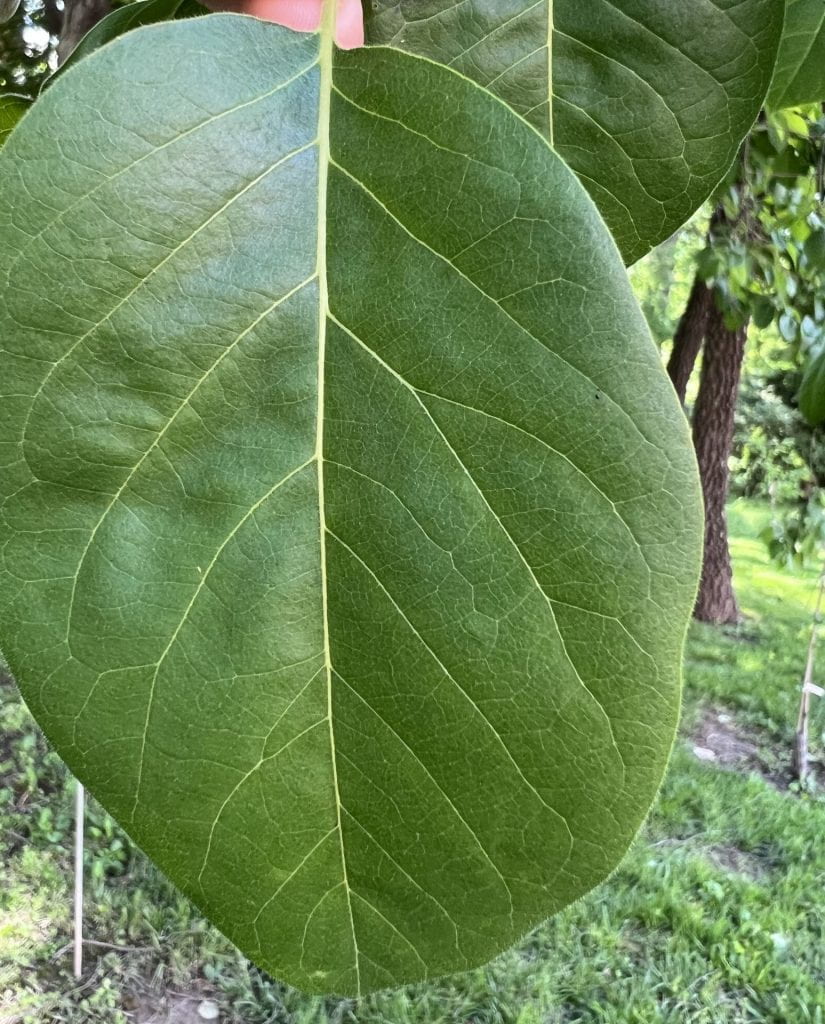
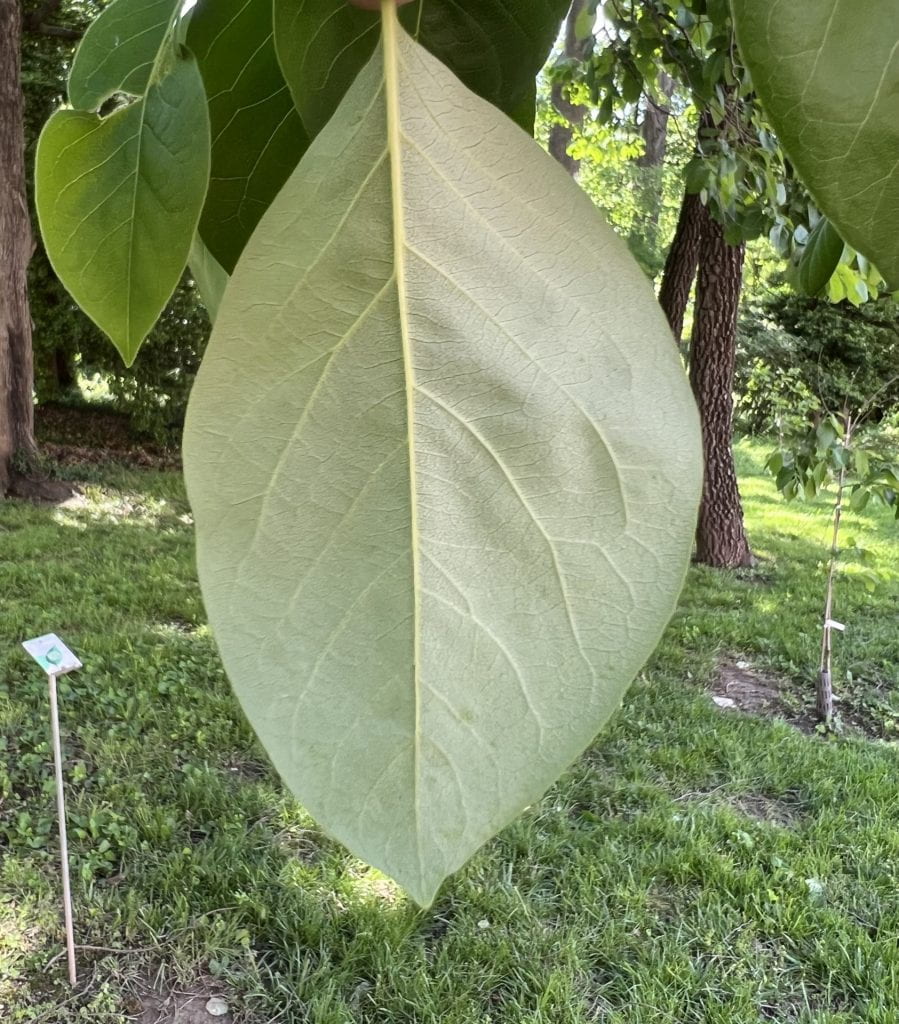
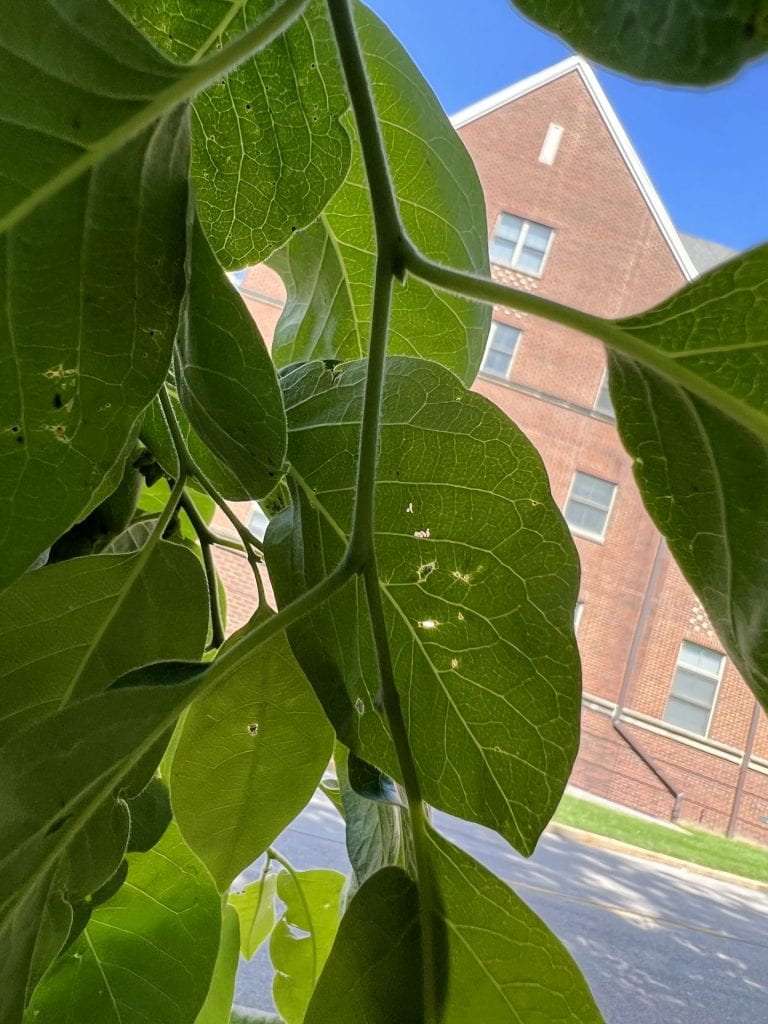
The leaf of the Persimmon is broadly elliptic with an acuminate (tapering) tip, dark green, and shiny. The underside of the leaf is pale green. The leaves are 3″-6″ in length, and arranged alternately on the stem. They turn yellow in the fall.
Twig and Bud Identification
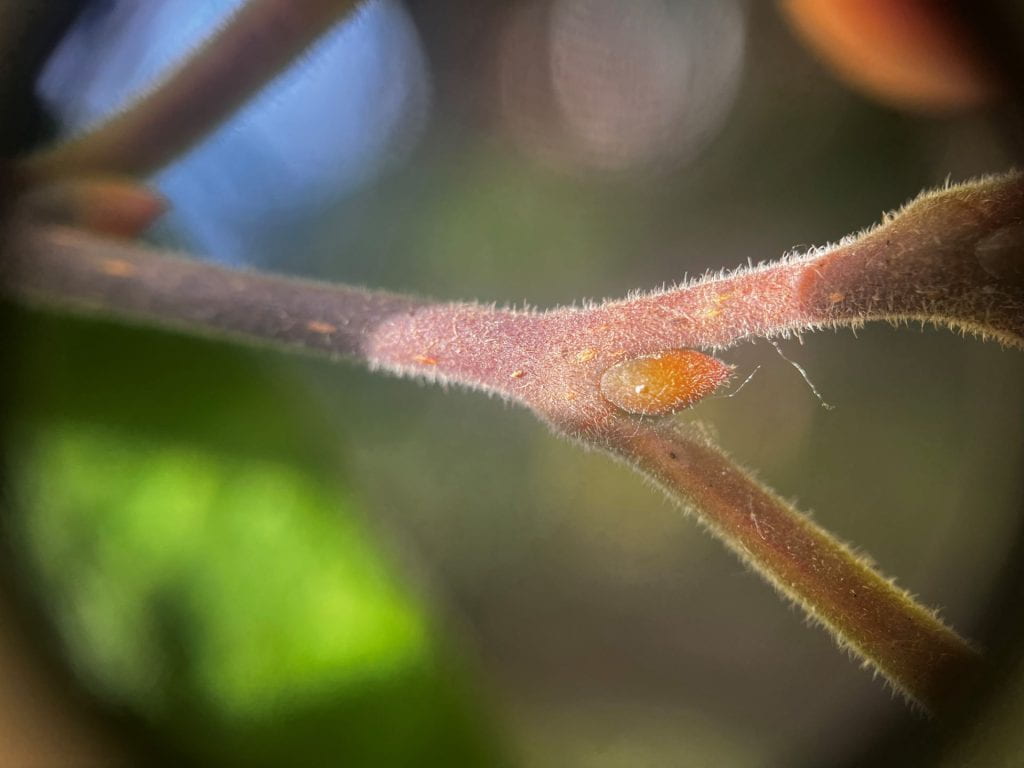
The twig is tan and zig zag. They are covered in dense hairs. The buds are orange-brown and also hairy. They have an ovate shate, slightly pointed at the tip.
Bark Identification
The bark is very distinctive, with deep, thick plates that create irregular furrows on the bark surface. The bark color is gray.
Fruit Identification
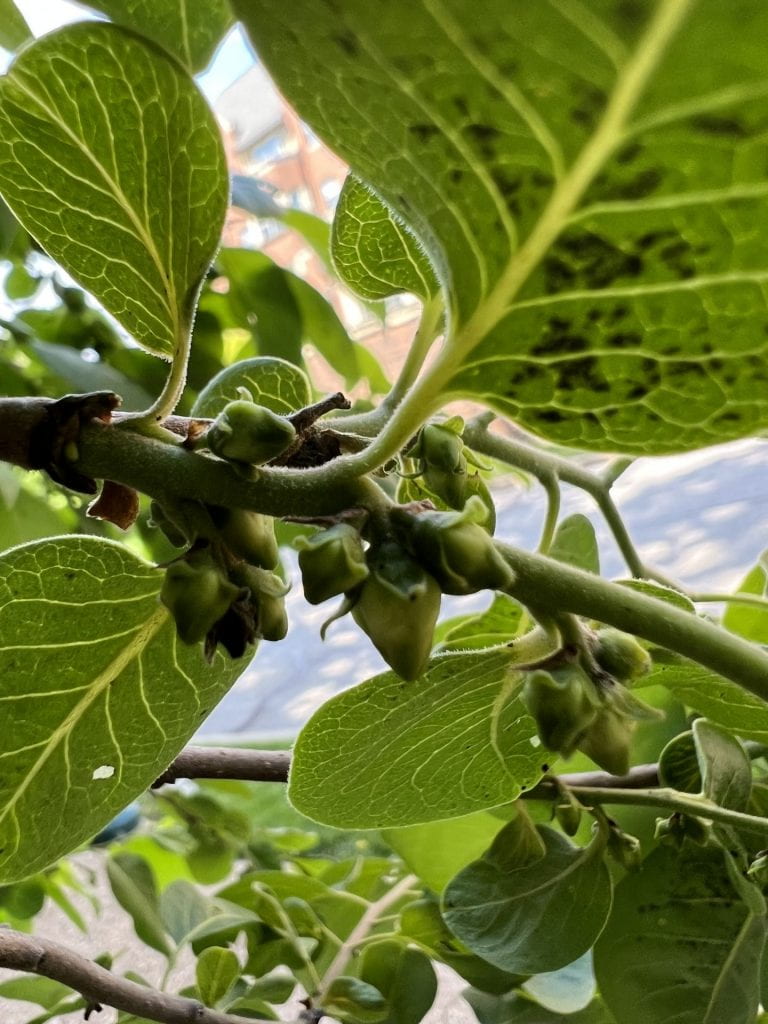
The fruit of the Persimmon is an yellow-orange ovoid berry up to 2″ wide. The fruit is edible when past ripe in late autumn and winter, but because the Persimmon is dioecious, only female trees will produce fruit.
Flower Identification
The flowers of the Persimmon are dioecious. The staminate (male) flowers are in small clusters, four-petaled, and cream-colored. The pistillate (female) flowers are also four-petaled and cream colored, but singular on the stem. The flowers have a pleasant scent and bloom in spring.